In the advent of big data where data is generated at unprecedented rates, traditional cloud computing architectures are facing new challenges but edge computing is here to the rescue. Edge computing is a shift that’s revolutionizing how we process and analyze data in real-time. This transformation is not just a technological evolution; it’s a necessary adaptation to meet the demands of our increasingly connected world.
The Evolution of Data Processing
The journey from centralized data centers to edge computing reflects the changing nature of our digital needs. While cloud computing brought unprecedented scalability and flexibility, the exponential growth of IoT devices and real-time applications has exposed its limitations. Latency, bandwidth constraints, and data privacy concerns have pushed computing capabilities closer to where data originates.
Understanding Edge Computing
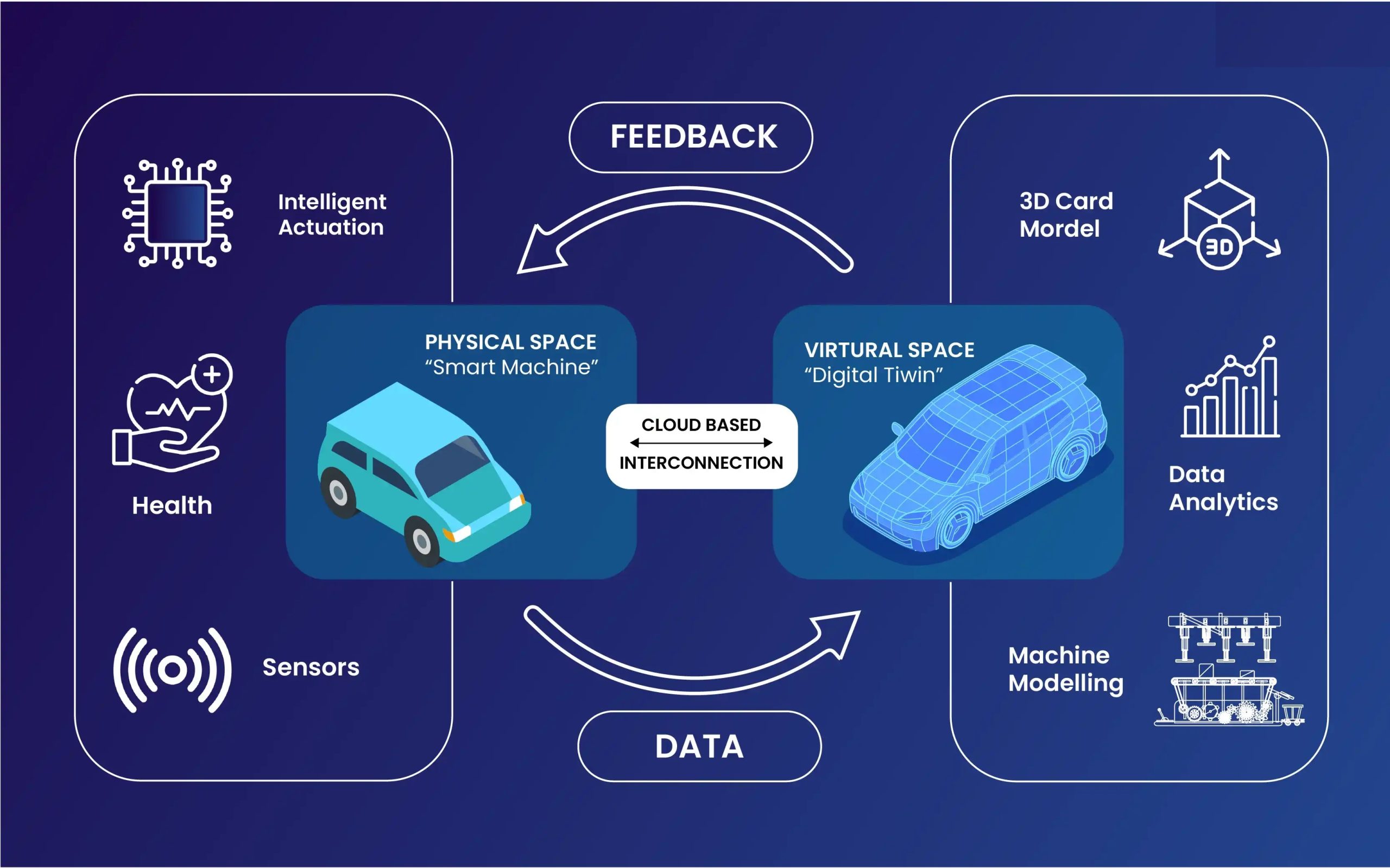
Edge computing brings computation and data storage closer to the location where it’s needed. Rather than relying solely on distant data centers, processing occurs at or near the source of data generation. This architectural shift offers several key advantages:

1. Reduced Latency
By processing data locally, edge computing significantly reduces the time between data collection and action. This is crucial for applications where milliseconds matter, such as:
- Autonomous vehicles requiring instant decision-making
- Industrial automation systems
- Augmented reality experiences
- Healthcare monitoring devices
2. Bandwidth Optimization
Edge computing helps organizations manage their network resources more effectively by:
- Filtering and processing data locally
- Sending only relevant information to the cloud
- Reducing overall data transmission costs
- Minimizing network congestion
3. Enhanced Security and Privacy
With data processed locally, edge computing provides:
- Better control over sensitive information
- Reduced exposure to internet-based threats
- Compliance with data localization requirements
- Improved regulatory compliance for sensitive sectors
Real-World Applications Transforming Industries
Manufacturing
Smart factories are leveraging edge computing to:
- Monitor equipment health in real-time
- Predict maintenance needs
- Optimize production processes
- Ensure quality control through immediate analysis
Healthcare
The medical sector is seeing revolutionary changes through:
- Real-time patient monitoring systems
- Immediate analysis of medical imaging
- Emergency response optimization
- Remote healthcare delivery
Smart Cities
Urban infrastructure is becoming more intelligent with:
- Traffic management systems
- Public safety monitoring
- Energy grid optimization
- Environmental monitoring
Challenges and Considerations
While edge computing offers tremendous potential, organizations must navigate several challenges:
Technical Challenges
- Hardware limitations and maintenance
- Complex system architecture design
- Network reliability and redundancy
- Security implementation across distributed systems
Operational Considerations
- Device management at scale
- Software updates and maintenance
- Resource allocation and optimization
- Cost management across distributed systems
The Future of Edge Computing
Looking ahead, several trends are shaping the evolution of edge computing:
1. AI and Machine Learning Integration
- Enhanced local processing capabilities
- Improved decision-making algorithms
- Automated system optimization
- Predictive maintenance and analytics
2. 5G Network Integration
- Increased bandwidth capabilities
- Lower latency communications
- Enhanced mobile edge computing
- New use cases and applications
3. Edge-Cloud Hybrid Solutions
- Seamless integration between edge and cloud
- Dynamic workload distribution
- Enhanced scalability
- Improved resource utilization
Implementation Strategies
Organizations looking to implement edge computing should consider:
Assessment and Planning
- Evaluate current infrastructure and needs
- Identify suitable use cases
- Develop clear objectives and metrics
- Create a phased implementation plan
Architecture Design
- Choose appropriate hardware solutions
- Design for scalability and flexibility
- Implement robust security measures
- Ensure redundancy and failover capabilities
Monitoring and Optimization
- Implement comprehensive monitoring systems
- Establish performance metrics
- Regular system optimization
- Continuous improvement processes
Wrapping Up
Edge computing represents a fundamental shift in how we process and utilize data. As organizations continue to generate more data and require faster processing times, the importance of edge computing will only grow. Success in this new paradigm requires careful planning, robust architecture, and a clear understanding of both the benefits and challenges involved.
The future of computing lies not in choosing between cloud and edge, but in creating harmonious systems that leverage the strengths of both. Organizations that successfully implement edge computing solutions today will be better positioned to meet the demands of tomorrow’s digital landscape.